3D printing in medicine is reshaping how we think about healthcare. Imagine doctors using a 3D printer to create patient-specific implants, lifelike anatomical models, and even experimental tissue structures. This technology isn’t just futuristic. It’s happening now, improving surgeries, speeding up treatments, and opening new possibilities in personalized care. As 3D printing continues to evolve, the medical field is stepping into an era where innovation meets precision, and patients benefit like never before.
Introduction to 3D Printing in Medicine and Healthcare
3D printing in medicine has transformed the healthcare industry with precise, patient-specific 3D printed models and devices. Through additive manufacturing, medical professionals can design customized medical devices that improve treatment outcomes. This 3D printing process also enables medical research to create accurate prototypes of medical devices. As innovation in printing technologies grows, the use of 3D printing in healthcare continues to expand, supporting advances in medical care and personalized medicine.
Overview of 3D Printing in Healthcare
In healthcare, 3D printers work to produce models to 3D scan and replicate human anatomy. This allows medical device manufacturers to create patient-specific medical devices and components. The technology in the medical field now includes 3D bioprinting for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Printing materials are carefully selected to match the properties of 3D anatomical structures. By using 3D printing technology, healthcare providers enhance both training and surgical outcomes.
Growth of 3D Printing in Medicine
The growth of 3D printing in medical applications has been fueled by advancements in 3D printing technologies and materials. Medical 3D printing also benefits from desktop 3D printers, making a 3D device prototype accessible to smaller clinics. Adoption of 3D printing in medical fields allows the production of medical devices and device components at lower costs. This innovation supports the future of 3D printing for medical research and customized treatments.
Did you know that doctors can 3D print lifelike heart models to plan surgeries?
Key Benefits of 3D Printing in the Medical Field
The benefits of 3D printing for medical use include faster development of patient-specific 3D printed models and better fit for customized medical devices. Medical applications of 3D printing improve accuracy in surgical planning. Printing technology in the medical field also supports medical training by providing realistic 3D printed anatomical models. Ultimately, 3D printing allows healthcare professionals to provide personalized medicine at an unprecedented level.
Applications of 3D Printing in Healthcare Industry
The applications of 3D printing in healthcare include creating medical devices, aiding surgical planning, and producing patient-specific drug delivery systems. Medical 3D printing can provide solutions that traditional manufacturing cannot achieve. Using 3D printing to create tailored implants or tools enhances patient safety and recovery time. The healthcare industry benefits from the variety of medical applications made possible by different 3D printing processes.
Read about Digital Smile Design
Medical 3D Printing for Customized Medical Devices
Customized medical devices are produced using 3D printing to meet patient-specific needs. 3D printing custom devices help reduce complications and improve fit. Medical 3D printing to produce prototypes of medical devices supports both innovation and efficiency. Desktop 3D printers and materials used for 3D printing medical equipment allow hospitals to respond quickly to urgent needs. This printing also reduces waste compared to traditional production methods.
Use of 3D Printing in Surgical Planning and Medical Imaging
In surgical planning, 3D printing applications offer patient-specific 3D printed models based on 3D scanning and 3D printing. These models help surgeons practice and refine techniques before operating. Medical imaging data is transformed into accurate 3D models, supporting medical training and improving patient-specific care. Printing to produce anatomical replicas has become a valuable tool for medical professionals worldwide.
3D Printed Tablets and Drug Delivery Solutions
3D printed tablets provide precise dosages tailored to individual patients. Using 3D printing technology in pharmaceuticals enables personalized medicine. The printing processes create complex drug release systems not possible with conventional manufacturing. Such medical applications improve treatment efficiency and adherence. In this field, 3D printing can provide innovative solutions for controlled drug delivery.
3D Printing Technologies and Materials in the Medical Field
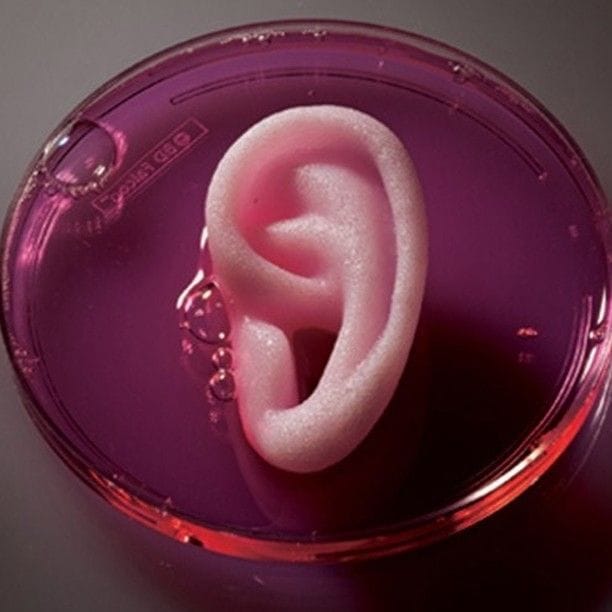
3D printing technologies and materials are central to the success of medical applications. Advances in 3D printing technology include dual-material 3D printed objects for complex structures. Materials used for 3D printing medical devices must meet strict safety standards. Different 3D printing methods, such as SLS 3D printers, are used for medical purposes. This combination of 3D printers and materials shapes the potential of 3D printing in the medical field.
Did you know that 3D printing is used to create personalized prosthetic limbs?
Advanced 3D Printing Technologies in Healthcare
Advanced printing technologies, including 3D bioprinting, enable tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Using 3D printing to create scaffolds for cell growth opens new possibilities in medical research. Printing technology in the medical industry now supports making a 3D organ model for testing and training. The potential of 3D printing to produce complex structures continues to grow with each innovation.
Common 3D Printing Materials for Medical Applications
Materials used for medical 3D printing include biocompatible plastics, metals, and bio-inks. These 3D printing materials match the properties of 3D tissues or bones. The choice of printing materials directly affects the quality and safety of medical devices and device components. Advances in medical materials allow the creation of patient-specific medical devices for various treatments.
Creating Accurate 3D Models for Medical Research
Creating medical devices and accurate 3D printed anatomical models supports innovation in medical research. Patient-specific 3D printed models allow researchers to study unique medical conditions. 3D printing applications also improve prototypes of medical devices for testing before human use. This combination of printing and medical research accelerates the development of new treatments.
Advantages and Benefits of 3D Printing in Medicine
The advantages of 3D printing include faster prototyping, reduced production costs, and highly customized solutions. Benefits of 3D printing in healthcare range from personalized medicine to enhanced surgical precision. Medical use of 3D printing allows doctors to adapt devices quickly to patient needs. This future of 3D printing for medical care promises even better outcomes.
Main Advantages of 3D Printing for Medical Use
Advantages of 3D printing include the ability to create patient-specific medical devices and anatomical models. Medical professionals use 3D printing to reduce surgery time and improve accuracy. Printing technology in the medical sector offers unique capabilities compared to traditional manufacturing.
Benefits of 3D Printing in Healthcare Industry
Benefits of 3D printing in the healthcare industry include innovation in treatment methods and faster production of medical equipment. 3D printing also allows cost-effective creation of prototypes and final devices. Medical device manufacturers benefit from the speed and flexibility of the 3D printing process.
How 3D Printing Applications Improve Patient Care
3D printing applications improve patient care by providing personalized medicine solutions. Using 3D printing technology, doctors create devices tailored to each patient’s anatomy. This approach reduces complications and enhances recovery speed.
Read also The End of Life on Earth
Challenges and Limitations of 3D Printing in Healthcare
Despite its potential, challenges of 3D printing remain. Technical and regulatory issues limit the widespread adoption of 3D printing in medical applications. Medical professionals must address risks and ensure patient safety before full-scale implementation.
Technical and Regulatory Challenges of 3D Printing
Technical barriers include ensuring the properties of 3D printed devices meet medical standards. Regulatory frameworks for medical applications of 3D printing are still evolving. Adoption of 3D printing requires compliance with strict guidelines.
Risks and Limitations in the Use of 3D Printing
Risks include device malfunction and material incompatibility. Used in medical care, 3D printing must pass rigorous testing. Printing to produce medical devices carries responsibilities for patient safety.
Addressing Barriers in Medical 3D Printing Adoption
Addressing these barriers involves advances in medical materials and training for medical professionals. The production of medical devices using 3D printing must meet industry regulations. Overcoming these challenges will support broader adoption.
Did you know that researchers are exploring 3D printed organs for future transplants?
Future of 3D Printing in Medicine and Healthcare
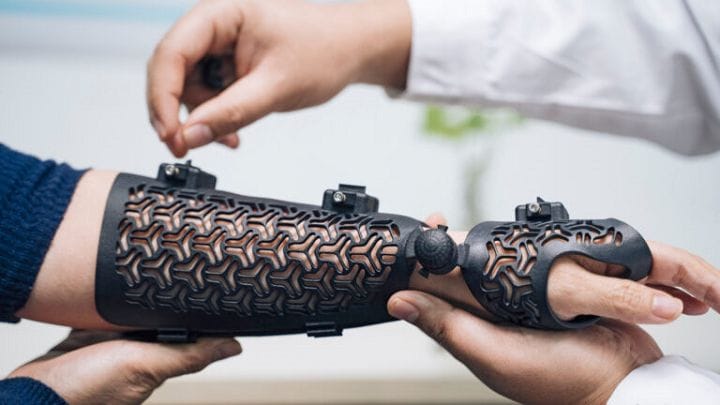

The future of 3D printing holds great promise for medical applications. Innovations in printing technology in the medical sector will lead to better devices and treatments. The potential of 3D printing for patient-specific care is significant.
Innovations Shaping the Future of 3D Printing
Innovations include advancements in 3D printing technique, 3D scanning and 3D printing integration, and new printing technologies. This will enhance personalized medicine and regenerative medicine solutions.
Potential in Customized Medical Devices and Treatments
The potential of 3D printing to create customized medical devices will transform the healthcare industry. Printing technology will improve the production of patient-specific medical devices and equipment.
Role of 3D Printing in the Future of Medical Research
3D printing applications will play a vital role in medical research. Models to 3D print complex organs will accelerate discoveries in treatment and diagnosis.
Frequently Asked Questions about 3D Printing in Medicine
How is 3D printing used in modern healthcare?
3D printing in healthcare creates patient-specific medical devices, surgical guides, and 3D printed anatomical models. Using 3D printing technology in the medical field also supports medical training, regenerative medicine, and production of medical equipment.
What is the future of 3D printing in healthcare?
The future of 3D printing for medical use includes advances in medical applications, tissue engineering, and customized medical devices. 3D printing allows patient-specific 3D printed models and medical devices to be produced faster and more accurately.
What medical products are 3D printed?
3D printed medical devices include prosthetics, dental implants, 3D printed tablets, and prototypes of medical devices. Materials used for 3D printing medical products vary from biocompatible plastics to metals for specialized medical applications.
The journey of 3D printing in medicine is only just beginning, and the potential feels limitless. From advanced surgical planning to groundbreaking regenerative medicine, every innovation brings us closer to truly personalized healthcare. So, the next time you hear about a 3D printer in a hospital, remember—it might just be shaping the future of medical treatment, one layer at a time. Are you ready to see what’s next?
Read about Scars Laser Treatment